本文已被:浏览 805次 下载 416次
Received:August 03, 2021 Published Online:February 20, 2022
Received:August 03, 2021 Published Online:February 20, 2022
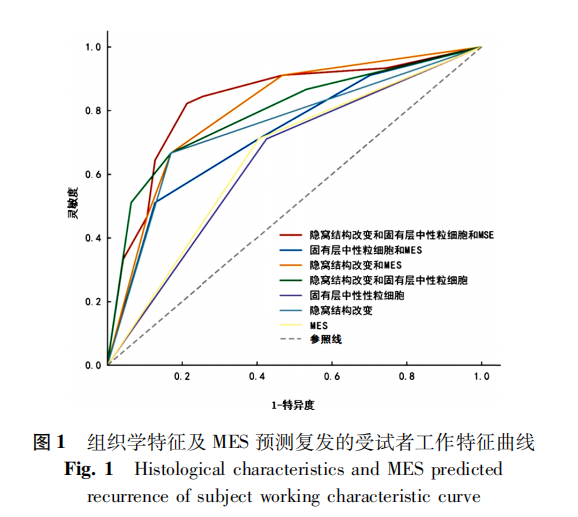
中文摘要: 目的 探讨临床缓解期溃疡性结肠炎(UC)患者复发与组织学特征的关系。方法 选取2016年1月至2019年12月潍坊市人民医院收治的92例临床缓解期UC患者,在结肠镜下所见炎症最重黏膜处进行组织活检,显微镜下观察其组织学特征,记录结肠镜检查后1年的临床结局,按随访期间是否复发分为复发组和非复发组,对比两组组织学特征,并绘制各因素预测UC复发的受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线),计算AUC、灵敏度、特异度。结果 共有51例(55.4%)患者未达到黏膜愈合。随访期间共45例患者复发,47例未复发。未复发组的黏膜愈合率高于复发组(59.6% vs 28.9%,P<0.01)。复发组隐窝结构改变、固有层浆细胞增多、固有层中性粒细胞增多比例高于未复发组(P<0.05)。Logistic回归分析显示,隐窝结构改变、固有层中性粒细胞增多、Mayo内镜评分(MES)均是预测UC复发的独立危险因素(P<0.05)。隐窝结构改变、隐窝结构改变+固有层中性粒细胞增多、隐窝结构改变+MES、固有层中性粒细胞增多+MES、隐窝结构改变+固有层中性粒细胞增多+MES的AUC值均>0.7,四项指标灵敏度分别为66.7%、66.7%、66.7%、55.1%,特异度分别为83.0%、83.0%、83.0%、78.7%。结论 临床缓解期UC患者中,内镜疾病活动和组织学活动之间相关性很低,隐窝结构改变及固有层中性粒细胞增多能有效预测临床复发。
Abstract:Objective To investigate the relationship between recurrence and histological features in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) in clinical remission. Methods Ninety-two patients with UC in clinical remission admitted to Weifang Peoples Hospital from January 2016 to December 2019 were collected, biopsied at the most inflamed mucosa was seen under colonoscopy, its histological characteristics were observed under a microscope. The clinical outcome of 1 year after colonoscopy was recorded. According to whether there was recurrence during follow-up, they were divided into recurrence group and non-recurrence group, and the histological characteristics of the two groups were compared, receiver operating characteristics (ROC curve) of each factor predicting UC recurrence was drawed to calculate AUC, sensitivity, and specificity. Results Overall, 55.4% of patients in clinical remission did not achieve mucosal healing. During the follow-up period, 45 patients recurred and 47 patients did not recur. The rate of mucosal healing in the non-recurrence group was higher than that in the recurrence group (59.6% vs 28.9%, P<0.01).The rates of crypt structural changes, lamina propria plasmacytosis, lamina propria neutrophilia were significantly higher in the recurrence group than those in the non-recurrence group(P<0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that crypt structure changes, lamina propria neutrophils increased, and Mayo endoscopic subscore (MES) were independent risk factors for predicting UC recurrence (P<0.05). The AUC values for crypt structural changes, crypt structural changes + intrinsic layer neutrophilia, crypt structural changes + MES, intrinsic layer neutrophilia + MES, and crypt structural changes + intrinsic layer neutrophilia + MES were>0.7. The sensitivity of the four indicators was 66.7%, 66.7%, 66.7%, and 55.1%, respectively, and the specificity was 83.0%, 83.0%, 83.0%, and 78.7%, respectively. ConclusionsThe correlation between endoscopic disease activity and histological activity was low in patients with UC in clinical remission, and saphenous fossa structural changes and lamina propria neutrophilia were effective predictors of clinical relapse.
keywords: Clinical remission Ulcerative colitis Histological features Mayo endoscopic subscore Recurrence
文章编号: 中图分类号:R574.62 文献标志码:A
基金项目:山东省潍坊市科技发展项目(2018YX002)
引用文本: